
Learning Label Modular Prompts for Text Classification in the Wild
Hailin Chen, Amrita Saha, Shafiq Joty, and Steven Hoi
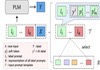
Machine learning models usually assume i.i.d data during training and testing, but data and tasks in real world often change over time. To emulate the transient nature of real world, we propose a challenging but practical task: text classification \textitin-the-wild, which introduces different non-stationary training/testing stages. Decomposing a complex task into modular components can enable robust generalisation under such non-stationary environment. However, current modular approaches in NLP do not take advantage of recent advances in parameter efficient tuning of pretrained language models. To close this gap, we propose \textsc\small{ModularPrompt}, a label-modular prompt tuning framework for text classification tasks. In \textsc\small{ModularPrompt}, the input prompt consists of a sequence of soft \emphlabel prompts, each encoding modular knowledge related to the corresponding class label. In two of most formidable settings, \textsc\small{ModularPrompt} outperforms relevant baselines by a large margin demonstrating strong generalisation ability. We also conduct comprehensive analysis to validate whether the learned prompts satisfy properties of a modular representation.
Learning Label Modular Prompts for Text Classification in the Wild
Hailin Chen, Amrita Saha, Shafiq Joty, and Steven Hoi. In the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP'22) 2022.
Abstract BibTex Slides
Hailin Chen, Amrita Saha, Shafiq Joty, and Steven Hoi. In the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP'22) 2022.
Abstract BibTex Slides