
CoHS-CQG: Context and History Selection for Conversational Question Generation
Xuan Long, Bowei Zou, Liangming Pan, Nancy Chen, Shafiq Joty, and Ai Ti
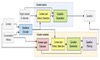
Conversational question generation (CQG) serves as a vital task for machines to assist humans, such as interactive reading comprehension, through conversations. Compared to traditional single-turn question generation (SQG), CQG is more challenging in the sense that the generated question is required not only to be meaningful, but also to align with the provided conversation. Previous studies mainly focus on how to model the flow and alignment of the conversation, but do not thoroughly study which parts of the context and history are necessary for the model. We believe that shortening the context and history is crucial as it can help the model to optimise more on the conversational alignment property. To this end, we propose CoHS-CQG, a two-stage CQG framework, which adopts a novel CoHS module to shorten the context and history of the input. In particular, it selects the top-p sentences and history turns by calculating the relevance scores of them. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performances on CoQA in both the answer-aware and answer-unaware settings.
CoHS-CQG: Context and History Selection for Conversational Question Generation
Xuan Long, Bowei Zou, Liangming Pan, Nancy Chen, Shafiq Joty, and Ai Ti. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING'22) , pages xx-xx, 2022.
PDF Abstract BibTex Slides
Xuan Long, Bowei Zou, Liangming Pan, Nancy Chen, Shafiq Joty, and Ai Ti. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING'22) , pages xx-xx, 2022.
PDF Abstract BibTex Slides