
Mind Your Inflections! Improving NLP for Non-Standard English with Base-Inflection Encoding
Samson Tan, Shafiq Joty, Lav R., and Min-Yen Kan
Morphological inflection is a process of word formation where base words are modified to express different grammatical categories such as tense, case, voice, person, or number. World Englishes, such as Colloquial Singapore English (CSE) and African American Vernacular English (AAVE), differ from Standard English dialects in inflection use. Although comprehension by human readers is usually unimpaired by non-standard inflection use, NLP systems are not so robust. We introduce a new Base-Inflection Encoding of English text that is achieved by combining linguistic and statistical techniques. Fine-tuning pre-trained NLP models for downstream tasks under this novel encoding achieves robustness to non-standard inflection use while maintaining performance on Standard English examples. Models using this encoding also generalize better to non-standard dialects without explicit training. We suggest metrics to evaluate tokenizers and extensive model-independent analyses demonstrate the efficacy of the encoding when used together with data-driven subword tokenizers.
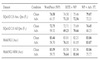
Mind Your Inflections! Improving NLP for Non-Standard English with Base-Inflection Encoding
Samson Tan, Shafiq Joty, Lav R., and Min-Yen Kan. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP'20) , pages 5647–-5663, 2020.
PDF Abstract BibTex Slides
Samson Tan, Shafiq Joty, Lav R., and Min-Yen Kan. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP'20) , pages 5647–-5663, 2020.
PDF Abstract BibTex Slides